使用机器学习和分子描述符进行NSAID分析的高级QSPR建模
作者:Gegbe, Brima
介绍
氨基芬是丙酸类别的非甾体抗炎药,其中还包括其他药物,例如布洛芬。Aminoprofen是通过用布洛芬的基本结构取代胺基化学设计的。氨基蛋白抑制酶环氧酶,该酶负责前列腺素的生物合成,体内的化学物质介导炎症,疼痛和发烧1,,,,2。氨基芬通过抑制前列腺素的产生来帮助减轻疼痛,减轻炎症和降低发烧。它通常是针对关节炎,肌肉疼痛和其他炎症性疾病的规定。药物可用于中度至上的疼痛问题,例如头痛和牙齿疼痛3,,,,4。与其他NSAID类似,氨基植物可能会产生不良影响,更长的使用,与胃肠道问题甚至心血管风险有关。氨基元的分子结构如图2所示。1(一个)。
Fenoprofen是属于丙酸药物类别的NSAID,例如布洛芬和萘普生。附着在丙酸的骨架上的苯氧基群有助于芬诺芬的药理作用。芬诺芬通过抑制酶环氧酶起作用,这对于疼痛,炎症和发烧的介体的介体而言,这对于合成前列腺素很重要。通过抑制前列腺素的合成,芬诺芬抑制了几种疾病状态的疼痛和炎症5,,,,6。它的适应症包括治疗类风湿关节炎,骨关节炎和轻度至中度疼痛,这可能是由肌肉骨骼损伤或月经痉挛引起的。与其他NSAID相似,fenoprofen可能会产生一系列不良反应,包括胃肠道刺激,心血管风险和肾功能障碍,特别是如果在一段时间内服用该药物的时间,或者在对这些问题易感性的情况下服用该药物7,,,,8。Fenoprofen的分子结构如图所示1(b)。
Flurbiprofen是一种非甾体类抗炎药,由丙酸衍生物,例如布洛芬和富富芬组成。它具有特定的化学特性;通过将氟原子的附着在丙酸骨架上的附着来增强其活性和特异性9,,,,10。弗拉伯利芬主要通过抑制COX酶,主要是Cox-1和Cox-2,这些酶负责产生前列腺素,脂质化合物,包括炎症,疼痛和发烧等过程18。氟吡芬用于治疗诸如类风湿关节炎和骨关节炎等疾病的管理,并有效地管理。此外,它可能减轻轻度至中度疼痛,包括牙齿疼痛和术后不适。存在局部眼科制剂,以防止或减少眼部手术后的炎症,并在手术过程中预防损伤11,,,,12。弗拉伯利酮的常见不良反应包括胃肠道刺激,头晕和头痛,请参见图。1。严重的风险包括心血管事件或长时间使用或易感人士的肾脏损害。弗洛比哌芬的分子结构如图所示1(c)。
布洛芬是丙酸的衍生物,是使用最广泛的NSAID之一。它是通过修饰异丁基苯在化学中合成的,在该异丁基苯二烯中引入了羧酸基团的结构,这对于其抗炎活性至关重要。布洛芬通过抑制COX酶,特别是Cox-1和Cox-2的作用,后来减少了前列腺素的产生,这些酶是炎症,疼痛和发烧的化学介质13,,,,14。布洛芬广泛用于轻度至中度疼痛,炎症减少和发烧。布洛芬被认为有效治疗头痛,月经痉挛,牙痛,肌肉疼痛,关节炎和其他肌肉骨骼疾病。它以片剂,胶囊,液体悬浮液和局部凝胶的形式存在。布洛芬通常具有良好的耐受性,可能具有副作用,例如胃肠道刺激,恶心,或很少与长期或高剂量使用相关的肾脏或心血管问题15,,,,16。通常建议用食物消费布洛芬,以避免胃部不适。布洛芬的分子结构如图2所示。2(一个)。
酮洛芬是NSAID,并在丙酸衍生物中分类,其中还包括布洛芬和萘普生。它是通过在丙酸骨架上修饰苯甲酰基来制备的,以增强其抗炎和镇痛活性17,,,,18。它通过抑制COX-1和COX-2(负责产生前列腺素的酶)来发挥其治疗作用,这些酶是疼痛,炎症和发烧的介体。使用酮洛芬的最常见适应症是类风湿关节炎,骨关节炎,强直性脊柱炎,其他骨和关节疾病的疼痛和炎症,以及其他疼痛疾病,例如术后,牙齿或抑郁症。剂型包括片剂,胶囊,局部凝胶和注射19,,,,20。尽管有效,但它可能有可能的副作用,例如胃肠道刺激,头晕以及一些心血管或肾脏故障,请参见图。2。它通常被处方用食物消费,或者根据医学专家的处方,以减轻可能的不良影响。酮洛芬的分子结构如图2所示。2(b)。
Loxoprofen是一种丙酸衍生物,一类非甾体类抗炎药,是东亚国家处方的最受欢迎的药物之一,尤其是日本21,,,,22。这是一个前药。给药后,它会在肝脏中经历代谢,形成一种活性化合物,称为反oH-氯氧蛋白,该化合物抑制了Cox酶。反过来,这又减少了前列腺素,疼痛,炎症和发烧的合成,通过loxoprofen抑制COX-1和COX-2。Loxoprofen用于治疗由类风湿关节炎,骨关节炎和肌肉骨骼损伤引起的疼痛和炎症。它在治疗轻度或中度疼痛的治疗方面具有多功能性,包括头痛,牙齿疼痛和痛经。Loxoprofen被用作口服片剂,局部凝胶和透皮贴片。因为它是前药,因此与其他NSAID相比,它会导致胃肠道不良事件少,因为它可以最大程度地减少胃部刺激23,,,,24。但是,与所有NSAID相似,长期给药可能会出现肾脏障碍甚至心血管事件的一些风险,尽管这些风险可能并不常见。Loxoprofen的分子结构如图2所示。2(b)。
连接到丙酸主链的萘组有助于抗炎和镇痛特性25,,,,26。具体而言,该药物通过抑制COX酶,特定于COX-1和COX-2来起作用,这些酶是造成前列腺素的合成的。它主要用于各种疾病,包括类风湿关节炎,骨关节炎,强直性脊柱炎,痛风和肌腱炎。通常,该药物用于治疗轻度至中度疼痛,其中包括头痛,月经抽筋,牙齿疼痛和肌肉的疼痛。在NSAIDS中,萘普生的半衰期相对较长。因此,大多数患者每天可以服用两次27,,,,28。它可以在许多制剂中使用,例如片剂,胶囊,液体悬浮液和扩展释放配方。尽管萘普生的耐受性良好,但胃肠道刺激,恶心或头晕可能会发生。长期或高剂量疗法可能会增加心血管不良事件,肾功能障碍或胃肠道出血的风险,尤其是在易感人群中,请参见图。3。通常,它是用食物或根据医疗保健提供者的指示来最大程度地降低风险的。萘普生的分子结构如图2所示。3(一个)。
pranoprofen是一种属于丙酸衍生物类别的非甾体类抗炎药。该分子的一般结构由带有附着苯基的丙酸主链组成,提供其特征性抗炎,镇痛和抗染料特性29。Pranoprofen抑制Cox酶的活性,主要是Cox-2,抑制了前列腺素的合成,这是疼痛,炎症和发烧过程中的关键参与者。pranoprofen在眼科中广泛使用,用作治疗与过敏性结膜炎,术后炎症和其他眼部炎症性疾病有关的炎症和疼痛。与口服NSAID相比30。它因其在减少眼部不适和炎症方面的功效而受到重视,同时保持了有利的安全性。Pranoprofen的分子结构如图2所示。3(b)。
Suprofen是NSAID,由于其镇痛和抗炎特性,它也经常使用。它通过抑制Cox酶发挥作用,从而降低了负责疼痛和炎症的前列腺素水平31。尽管以前有口服形式可用于关节炎治疗以及轻度至中度疼痛,但其目前的主要应用是眼科溶液的形式。该形式用于治疗术后眼部炎症或预防眼部手术中的菌症32。Suprofen对于提供最小的全身副作用的局部缓解局部缓解局部缓解尤其有价值。超芬的分子结构如图5(c)所示。
通常耐受性良好,可能会引起较小的副作用,例如眼睛刺激,发红或施用时燃烧的感觉。通常在医疗专业人员的指导下开处方pranoprofen,建议用户对剂量保持谨慎,以避免并发症。非甾体类抗炎药(NSAIDS)是一类广泛用于缓解寒冷,流感,扭伤,头痛,菌株和疼痛时期症状的药物,通过降低炎症和降低温度。要开发的第一批NSAID是根据1829年的水杨酸盐,当时水杨酸盐是由一位德国科学家成功隔离的。他们的年销售额可以估计NSAID的重要性,美国柜台销售中有超过300亿的处方33。最突出的NSAID类是丙酸衍生物,包括氨基酸,富苯前,Flurbiprofen,Loxoprofen,Ketoprofen,Ibuprofen,inoprofen,Naproxen,pranoprofen和Suprofen。从化学上讲,这些化合物包含2-芳占中心官能团,其立体中心位于丙酸酯部分的alpha位置。主要是NSAIDS目标\(Cox-1 \)和\(COX-2 \)并通过其抑制作用。考克斯负责产生前列腺素,负责炎症的化学物质,并因抑制其产生而抑制其产生考克斯。
前列腺素介导炎症,导致疼痛,水肿和血管舒张。药物通过抑制这些化合物发挥抗炎作用,并产生镇痛作用34。抑制\(Cox-1 \)通过NSAIDS导致肾功能和血小板聚集降低,而抑制\(COX-2 \)导致骨形成和愈合过程。NSAID在具有上限效果方面是独一无二的。因此,在这种情况下由于无效性无效而导致严重伤害造成的疼痛,不建议它们。这些药物没有上瘾的潜力,并且不负责镇静或呼吸压力。为了从NSAID中获得所需的结果,他们的剂量已调整;出于镇痛的目的,给予较低剂量,而对于抗炎作用,需要较高剂量35。除了镇痛和抗炎目的外,还提出了NSAID的阿尔茨海默氏病(广告),患有记忆力丧失症状的老年人的痴呆症疾病,功效程度不同。广告来自聚集的结果\(\ beta \)淀粉样蛋白蛋白的前体进入低聚物,薄片和原纤维,这些构型对神经元具有剧毒,并限制其功能。一些研究也报道了\(\ alpha \ beta \)低聚物36,,,,37是导致的主要神经毒素广告在老人38,,,,39。在大多数情况下,治疗广告专注于预防\(\ alpha \ beta \)原纤维和低聚物形成,这种策略是有效的。未来的药物开发过程应集中在此策略上。NSAIDS通过类似现象起作用,发挥抗聚集活性并防止形成神经毒性的构象\(\ alpha \ beta \)肽40。在丙酸衍生的NSAID中,萘普生具有最大的抗聚集作用,并防止形成\(\ alpha \ beta \)床单,而其他床单包括酮芬和布洛芬41,,,,42。
在数学中,图g是一个点的集合,称为顶点v((g)和称为边缘的线e((g),将它们连接。图形已用于在多个研究领域的关系和结构进行建模,包括计算机科学,生物学和社交网络分析。程度\(d_ {v} \)图中的顶点的定义为连接到其的边数。例如,在任何顶点的无方向图中,顶点的度数为3。在有向图中,该度将指向顶点的位置边缘分开,并指向朝向它的高度边缘。顶点的程度提供了图形连接性的重要度量,学位分析可以披露网络中的集线器或关键节点。在图中,两个顶点之间的距离是连接它们的最短路径的长度,该路径被横穿的边数计数51。该度量对于图形偏心率的概念很重要,在该概率的概念中,对于顶点,它是该顶点到图中任何其他顶点的最大距离。偏心率提供了有关中央或外围顶点如何在图内的洞察力。最小偏心率的顶点称为图的中心,因为它位于中心位置52。这些概念在分析图结构(例如确定最短路径,瓶颈或网络效率)方面非常重要。
古特曼(Gutman)和波兰斯基(Polansky)介绍了第一个和第二个萨格勒(Zagreb)指数43作为
$$ \ begin {Aligned} m_ {1}(g)= \ sum \ limits _ {ab \ in E(g)}(\ wideHat {\ pi} {\ pi} _a + \ wideHat {\ pi} _b)e(g)}(\ wideHat {\ pi} _a \ times \ wideHat {\ pi} _b)\ end end {aligned} $$
Furtula和Gutman介绍了被遗忘的索引44作为:
$$ \ begin {Aligned} f(g)= \ sum \ limits _ {ab \ in E(g)} [((\ wideHat {\ pi} _a)_a)^2 +(\ wideHat {\ pi} _B)
Hyper-Zagreb指数由Rajasekharaiah等人引入。45作为
$$ \ begin {Aligned} hm(g)= \ sum \ limits _ {ab \ in E(g)}(\ widehat {\ pi} {\ pi} _a _a+\ wideHat {\ pi} {\ pi} _b)_b)
Rajini提出了第一个,第二和第三个重新定义的指数46如下:
$$ \ begin {aligned} rezg_1(g)=&\ sum \ limits _ {ab \ in e(g)} \ frac {\ wideHat {\ pi} _a+\ \ \ \ \ wideHat {\ pi} {\ pi}} _b},\\ rezg_ {2}(g)=&\ sum \ limits _ {ab \ in E(g)} \ frac {\ wideHat {\ wideHat {\ pi} _a \ times \ times \ times \ wideHat} _b},\\ rezg_ {3}(g)=&\ sum \ limits _ {ab {ab \ in E(g)} \ big(\ wideHat {\ pi} _a \ times \ times \ times \ wideHat} _b \ big)。\ end {Aligned} $$
拓扑指数是与化学结构相关的数值,可用于预测化合物的各种特性和活性。最近的研究探索了这些指数在不同药物类别的定量结构 - 特制关系(QSPR)分析中的应用。Shirakol等。47研究了基于距离的拓扑指数,而Gnanaraj等人。48专注于非甾体类抗炎药的基于学位的指数。Mondal等。49拟议的新型基于邻里学位的描述符,并为其计算开发了一种算法。Sardar和Hakami50使用回归模型将拓扑指数应用于阿尔茨海默氏病药物,以将结构特征与理化特性相关联。他们的研究发现,RandIC指数,第一个Zagreb指数和原子键连接指数对于理解结构活性关系特别有用51。这些研究表明,拓扑指数在药物发现和设计中的潜力,提供了对复合特性的见解,同时最大程度地减少了实验成本。
Almohanna等。52借助复杂的曲线拟合模型,证明了拓扑描述符与碳同素同质子的吉布斯自由能的相关性。Almohanna等。指出拓扑指数指向纳米材料热力学特性建模的预测值。Huang等。53应用机器学习算法,包括多个回归模型和XGBOOST,以对青光眼药物进行QSPR建模。他们的研究证明,复杂的算法可有效根据分子描述预测药理特性。Tamilarasi和Balamurugan54对抗真菌药物进行了QSPR和QSTR建模,以使用拓扑描述源来分析其毒性和药代动力学特征。Tamilarasi和Balamurugan的工作证明了图理论描述符在药物疗效和毒性预测中的功效。秦等人。55通过基于Python的拓扑建模方法对肺癌药物进行了QSPR研究。结果增强了药物优化和财产预测中基于计算机的工具和拓扑描述源的强度和潜力。Hakeem等。56通过基于基于度的分子描述符的QSPR模型,提供了对类黄酮分子结构的计算见解。这项工作增强了基于描述符方法在解释和预测生物活性化合物的行为方面的重要性。秦等人。57创建了一个基于Python的QSPR模型,以预测基于拓扑描述符的抗心律失常药物的物理化学特性。秦等人的工作。支持计算建模的应用以使药物分析过程更有效。Arockiaraj等。58进行了一项QSPR研究,比较学位,邻里和反向程度的药物指数,用于治疗肺癌。Arockiaraj等人的工作。提供了与药物相关特性建模中不同拓扑描述源相对优越性的证据。
结果与讨论
在本节中,我们使用一系列拓扑指数介绍我们的分析,以表征所考虑的药物的分子结构。下表包括这些指数的计算值,这些值对于表征所考虑的化合物的化学物质和可能的生物活性而变得很重要。在表中1,一系列基于学位的拓扑指数,包括被遗忘的指数\(f(g)\),超Zagreb索引\(hm(g)\),第一和第二萨格勒指数\(m_ {1}(g)\)和\(m_ {2}(g)\),以及第一个,第二和第三个重新定义Zagreb指数\(rezg_ {1}(g)\),,,,\(rezg_ {2}(g)\), 和\(rezg_ {3}(g)\),计算并包括。所有这些指数均以各自的公式进行计算,包括在分子图边缘上的求和并占据顶点。\(\ wideHat {\ pi} _ {a} \)和\(\ wideHat {\ pi} _ {a} \)考虑到。例如,被遗忘的索引\(f(g)\)通过对顶点的求和度进行计算,对于超Zagreb索引\(hm(g)\),考虑到顶点程度的正方形。
下表2呈现基于偏心性的拓扑描述符,例如偏心连接指数\(\ rho(g)\),偏心距离总和\(\ zeta(g)\),修改了第一个Zagreb索引\(m_ {1}(g)\),增强偏心连通性指数\(aug_ {n}(g)\)和偏心的Zagreb指数\(m _ {\ rho}(g)\)。所有这些描述符都呈现有关分子结构的空间处置和连通性以及此类结构的预测的信息,这对于预测药物和受体的相互作用和药代动力学都很重要。所有这些计算都是通过偏心率的顶点使用的,该值是代表顶点与图中其他任何其他距离之间最大距离的值。使用这些公式,可以在药物拓扑描述符之间进行比较分析,这将简化用于药理学研究的候选者的选择。所有这些结果验证并揭示了拓扑描述在发现和开发药物方面的效率,以及用于预测分子复杂性和行为的数值工具。
药物的理化特性,例如表中列出的药物3从Chemspider获得,这是一种公认的化学信息来源。这种物理化学特性中包括沸点,蒸发焓,极化性和表面张力,以及这种物理化学特性在描述环境中的行为时至关重要。沸点值提供了有关液态和气体状态之间化合物过渡的温度的信息,以及诸如纯化和蒸馏等过程中的过渡问题。蒸发焓描述了在液态下化合物的蒸发的值,并且这种价值告知药物中分子间力的变化。
分子可以弯曲的易度性是其极化性表示的,这对于解释生物系统过程和创建药物的输送系统至关重要。表面张力指导药物的润湿和扩散行为,并在半固态状态和液态状态下制定药物(例如,在乳霜和悬浮液中)发挥重要作用。Chemspider提供了此类特性的完整图片,并且可以预测药物的溶解度,生物利用度和稳定性,这对于药物开发至关重要。
线性回归
简单的线性回归是一种统计方法,用于解释一个变量与一个解释变量之间的关系,目的是预测单个解释变量的值处于了解状态时,以预测一个变量的值。
$$ \ begin {Aligned} y = \ beta _0 + b x + \ epsilon \ End {aligned} $$
其中y是要预测的变量,x是预测变量,\(\ beta _0 \)是拦截,\(b \)是坡度,\(\ epsilon \)是错误变量。线性回归试图估计\(b \)和\(\ beta _0 \)以一种方式,它可以最大程度地减少预测和实际y值之间的偏差。派生的回归方程产生了拓扑指数的变化控制沸点,蒸发焓,极化性和表面张力的方式的定量图。可以利用各种统计措施来测试和检查线性模型的性能和准确性。
-
确定系数((\(r^2 \)):这是因变量中的方差比例,可以通过使用自变量来预测,并且可以在0到1之间进行范围,而高值表示强拟合。
-
坡((\(b \)):这是因变量的一个单元更改,用于独立变量中的单个单位变化。
-
截距((\(\ beta _0 \)):当所有自变量均值为零时,因变量的值
-
p值:它显示了自变量在预测因变量时的重要性水平。低p值(通常<0.05)表明有显着的预测变量。
-
标准错误:这是系数的估计准确性的量度,值代表较小值的准确性较小。
我们在这项工作中进行了SPSS软件线性回归分析,并以系统形式获得并评估了回归方程。与输出相一致的物理化学和拓扑指数关系很强,为药物的开发和设计提供了有用的信息。
财产回归分析\(bp \),,,,\(ev \),,,,\(p \), 和\(英石\)显示在表中4。高值\(r^2 \)(范围在0.795至0.865之间)验证模型中捕获的依赖者的差异比例很高。F统计数据的高值和两个值的值\(bp \)和\(ev \)两者的值0.001值\(p \)和\(英石\)验证模型是重要且可靠的。不同系数\(一个\)和\(b \)对于替代性能,具有很高的价值\(bp \)(69.902),验证了预测变量的高影响\(bp \)。标准误差的足够低值(\(s_e \))验证模型的高可靠性。表中列出了分析特性的强预测值和意义4。
桌子中的趋势5与桌子中的那些相似4,\(r^2 \)值范围为0.785 0.861。所有F统计量的值为0\(bp \)和\(ev \)两者的0.001\(p \)和\(英石\)。所有系数\(一个\)和\(b \)在表中5与表中的系数略有不同4,价值较小\(一个\)(0.738),但价值更大\(b \)(89.730)。这是倾斜度较小的表达,但总体上对预测变量的总体贡献\(bp \)。所有标准错误在表中都有相似的值4,表明模型性能不会改变。表中的所有值5验证表中的值4,由于数据集和环境中可能发生的变化,可能发生的系数变化很小。
6重申高值\(r^2 \)(0.794至0.854)和F统计的显着值,值\(sig \)两者的0\(bp \)和\(ev \)两者的0.001\(p \)和\(英石\)。系数的变化很小\(一个\)和\(b \)两个系数的价值更大\(bp \)(3.988)与前面的表相比,反映了该数据集中较大的斜率。两者的标准错误都有很小的增加\(bp \)和\(ev \),强大而重要的模型占上风。表格中有进一步的演示6预测因子和属性之间具有特定于数据集的较小变化的牢固关系。
7以0.773 0.855的范围来证实前面的表\(r^2 \)值。所有F统计量都很重要,值为\(sig \)在0\(bp \)和\(ev \)两者的0.002\(p \)和0.001\(英石\)。系数\(一个\)和\(b \)两者\(bp \)和\(ev \)遵循与表格类似的模式6,但两者都有显着差异\(p \)和\(英石\)最明显的是系数的值\(b \)为了\(英石\)(11.137),一个比前面表中大的值,这表明预测变量对\(英石\)在这种情况下。标准误差的值与前面表中的标准误差相似,确认可靠的模型估计值。
属性值的回归分析\(bp \),,,,\(ev \),,,,\(p \), 和\(英石\)显示在表中8。所有值\(r^2 \)范围在0.773和0.855之间,代表模型中目标变量中的很大一部分。F统计量的所有值都很重要,具有\(sig \)两个物业为0\(bp \)和财产\(ev \),两个物业的0.002\(p \)两个物业的0.001\(英石\),支持模型固体。系数的可变性\(一个\)和\(b \)是针对各种财产类型的经验,具有很高的系数价值\(b \)用于财产\(bp \)(109.867)代表预测变量对属性的有力贡献\(bp \)。标准错误的所有值(\(s_e \))相对较低,支持模型的可靠性。表中有统一的预测价值和显着性8,系数变化很小,可能代表数据集中的特定属性类型。
高值\(r^2 \)在表中9,在0.785到0.861之间,验证了模型的强大解释能力。F统计数据的所有值都很重要,值为\(sig \)0两者\(bp \)和\(ev \)两者的0.001\(p \)和\(英石\)。系数的差异\(一个\)和\(b \)对于两个表都出现,系数的值较小\(一个\)(0.738),但系数的值较大\(b \)(89.730)\(bp \)。这是预测因子对\(bp \)。标准误差的一致值验证恒定模型性能。总体而言,桌子9验证并加强了前表中的观察结果,该观察结果可能是由于数据集和实验设置的差异所致。
10presents the regression analysis results for assets\(bp \),,,,\(EV\),,,,\(p \), 和\(英石\)。High values for\(R^2\)between 0.764 and 0.858 indicate that the model explains a high variance in the dependent variable.High values for the F-statistic, with values for\(Sig\)of 0 for both values for\(bp \),,,,\(EV\)and 0.002 for both values for\(p \)and 0.001 for both values for\(英石\), confirm the validity of the model.Varying the coefficients\(一个\)和\(b \)for each property, with a high value for\(bp \)(134.858), represents a high impact of the predictor variable for\(bp \)。Low values for the standard errors (\(S_E\)) confirm trust in the model, with strong predictive values and signs, in agreement with the trends in the preceding tables, such as Table10。
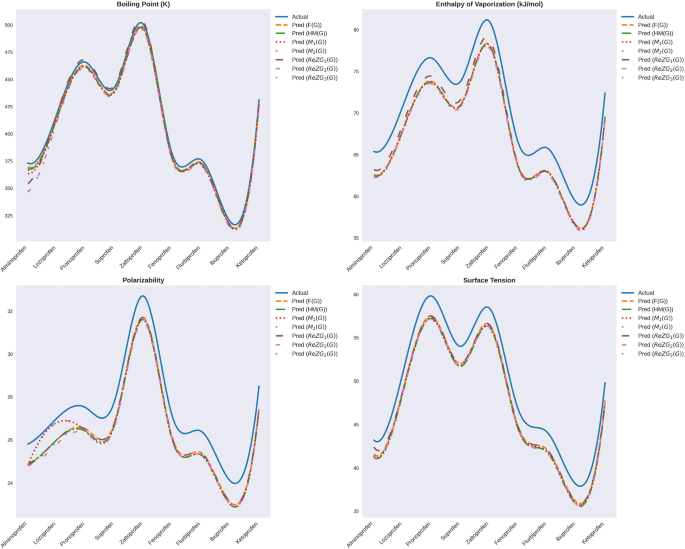
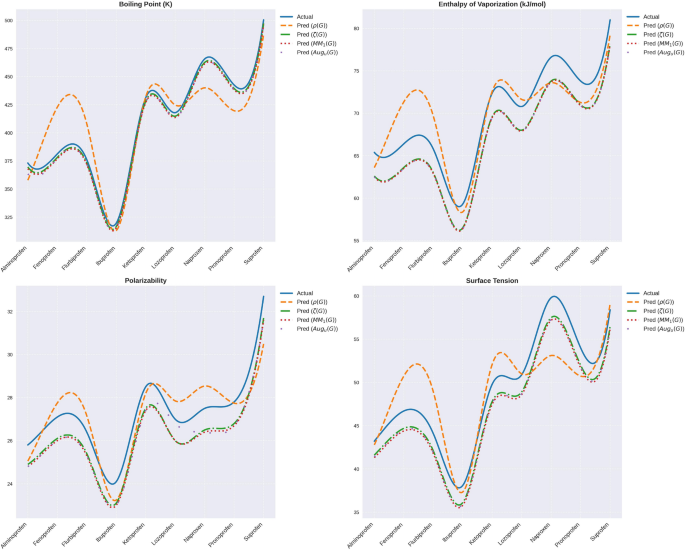
数字4presents a comparative examination of the predicted and experimental values of various physicochemical descriptors (boiling point, vaporization enthalpy, polarizability, and surface tension) for the collection of drugs.Prediction was conducted using a variety of graph descriptors, including\(F(G)\),,,,\(HM(G)\),,,,\(M1(G)\),,,,\(M2(G)\),,,,\(ReZG1(G)\),,,,\(ReZG2(G)\), 和\(ReZG3(G)\)。The actual and predicted values were contrasted in plots in a model performance and accuracy analysis.
1. Boiling Point (K):
-
The boiling points exhibit a definite trend down through drugs, with a boiling point for Zaltoprofen and a boiling point for Ibuprofen.
-
All values predicted closely follow actual behavior with minimum deviation.There was a relatively large deviation in the case of\(ReZG1(G)\)和\(ReZG2(G)\)for Zaltoprofen and Suprofen, respectively.
-
这\(F(G)\)和\(HM(G)\)models both seem to best fit, most closely tracking actual values for all drugs.
2. Enthalpy of Vaporization (kJ/mol):
-
The actual values for enthalpy increase steadily through to Zaltoprofen, with Zaltoprofen having a high value for enthalpy.
-
The values calculated for all of them closely mimic real trends, with both\(F(G)\)和\(HM(G)\)both having best-fit trends.The ReZG3(G) model underpredicts Zaltoprofen with a narrow margin, but both model values for\(M1(G)\)和\(M2(G)\)。
3. Polarizability:
-
The experimental values of real polarizability range relatively little for drugs, with Zaltoprofen possessing a largest value for polarizability.
-
The values calculated in all the models closely follow actual values, representing high accuracy in predicting polarizability.
-
The ReZG1(G) and ReZG2(G) model have negligible discrepancies, a sign of its effectiveness in predicting such a property.
4. Surface Tension:
-
The real values for surface tension exhibit a continuous rise from Alminoprofen through Zaltoprofen, with Zaltoprofen possessing a high value for surface tension.
-
The values calculated in all models closely follow the actual trend, with greatest accuracy in case of\(F(G)\)和\(HM(G)\)型号。
-
The ReZG3(G) model overpredicts a bit for Zaltoprofen, but everything else is in agreement with experimental values.
Models (\(F(G)\),,,,\(HM(G)\),,,,\(M1(G)\),,,,\(M2(G)\),,,,\(ReZG1(G)\),,,,\(ReZG2(G)\), 和\(ReZG3(G)\)) demonstrate strong predictive capabilities for the physicochemical properties of drugs.这\(F(G)\)和\(HM(G)\)models make the most dependable prediction for all of them, following the actual values most closely.Overall, the ReZG models represent drugs accurately, but with small discrepancies for individual drugs, namely the boiling point and surface tension.The smooth curve generated through interpolation reveals strong trends and deviations, and model performance comparisons become easier.The success in predicting physicochemical properties and future utility in drug development and materials science, as well as improvements in accuracy and utility, signifies that graph-based methodologies are strong tools for predicting physicochemical property values.The actual and predicted values are listed in Tables11和12。
桌子13shows the regression analysis for the four factors BP, EV, P, and ST.The coefficients (A and B) represent the direction of the association between the independent and dependent factors.The values for R represent a strong-to-high level of association, with a minimum for BP (0.586) and a maximum for EV (0.905).The values for\(R^2\)represent a high level of explained variance, with a high level of EV (0.819) and a high level of BP (0.824).All F-statistic values are significant (\(p < 0.05\));therefore, all models are significant at the\(p < 0.05\)等级。\(S_R\)was high for BP, representing a high variation in the prediction.
在表中14, the regression analysis reveals a better value for R than in Table13, with the best values for BP and P (0.896 and 0.898, respectively).High values of\(R^2\)confirm that a high proportion of the variance in the models is explained.The high F-statistic values verify that the models are valid.Most prominently, ST carries a negative value for its B coefficient (-1.288), which is indicative of an inverse relationship.The value of its standard error is relatively high for BP, which is a sign of prediction variation.
15shows high values for all but one property, with the largest values of R for BP and ST (0.886 and 0.890, respectively).All values for\(R^2\)confirm a high variance in the model, most notably for BP (0.754) and EV (0.744).All values for the F-statistic validated the accuracy of the model.The maximum value for the standard error was for BP, depicting a larger variation in the prediction.All p values were less than 0.05, confirming that the model was statistically significant.
16shows high values for all properties, with EV and BP having the highest values for R (0.844 and 0.849, respectively).The values for\(R^2\)show high variance in the models, with high values for P (0.897).All F-statistics values are high, confirming that the models are reliable.For BP, a high variation in prediction is shown, with the greatest value for the standard error.All p-values are less than 0.05, confirming that the statistics for the models have high values.
在表中17, through regression analysis, strong relations for all of them are observed, with the largest values for R (0.932 and 0.930, respectively, for BP and EV).All values of\(R^2\)indicate that the models have a high proportion of variance, most notably for BP (0.869) and EV (0.866).All had high values for F-statistics, confirming the validity of the model.All values for the standard error were relatively low, indicating less variance in the prediction.All p values were less than 0.05, confirming the statistical significance of the model.In general, the tables present strong and significant statistics between dependents and properties, with variation in prediction accuracy in terms of the standard error.
数字5和桌子18compare the actual values of these properties with the predicted values obtained from the different models (\(\rho (G)\),,,,\(\zeta (G)\),,,,\(MM_1(G)\), 和\(Aug_u(G)\))。The following is a discussion of the figure.Boiling Point (K)
-
Actual vs. Predicted: The actual boiling points are plotted against the predicted values from four different models.The predictions from the\(\zeta (G)\)和\(MM_1(G)\)models closely follow the actual values, indicating a high accuracy.这\(\rho (G)\)和\(Aug_u(G)\)models also show reasonable agreement but with slight deviations.
-
趋势: The boiling points generally increase across the drugs, with Suprofen having the highest boiling point.The models captured this trend well, although there were minor discrepancies for specific drugs such as ibuprofen.
Enthalpy of Vaporization (kJ/mol)
-
Actual vs. Predicted: The actual enthalpy values are compared with predictions from the four models.这\(\zeta (G)\)和\(MM_1(G)\)models again showed the closest alignment with the actual data.这\(\rho (G)\)和\(Aug_u(G)\)models perform well but with some overestimation for certain drugs.
-
趋势: The enthalpy of vaporization increases across the drugs, with Suprofen again having the highest value.The models effectively captured this increasing trend, with minor variations.
Polarizability
-
Actual vs. Predicted: The actual polarizability values are plotted alongside the predictions.这\(\zeta (G)\)和\(MM_1(G)\)models provide the most accurate predictions, closely following actual data.这\(\rho (G)\)和\(Aug_u(G)\)models also perform well but show slight underestimation for some drugs.
-
趋势: Polarizability values increase across the drugs, with Suprofen having the highest polarizability.The models accurately reflected this trend with minimal deviation.
表面张力
-
Actual vs. Predicted: The actual surface tension values are compared with the predicted values.这\(\zeta (G)\)和\(MM_1(G)\)models showed the best agreement with the actual data.这\(\rho (G)\)和\(Aug_u(G)\)models also perform well but with some overestimation for certain drugs.
-
趋势: Surface tension values generally increase across the drugs, with Naproxen and Suprofen having the highest values.The models captured this trend effectively with minor discrepancies.
-
Model Performance: 这\(\zeta (G)\)和\(MM_1(G)\)models consistently provide the most accurate predictions across all properties, closely following the actual data.这\(\rho (G)\)和\(Aug_u(G)\)models also perform well but with slight deviations.
-
Trends and Accuracy: The models effectively capture the increasing trends in the physicochemical properties across the drugs.Minor discrepancies were observed for specific drugs;however, overall, the predictions were reliable.
-
可视化: The use of smooth curves enhances the readability of the trends, and the grid layout allows for easy comparison across different properties.The legend and grid lines further improve the clarity of the figure.
Artificial neural network (ANN)
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)are computer models inspired by the structure and function of biological neural networks such as the human brain.They consist of layers of interconnected nodes or neurons that process the input data through weighted connections and activation functions.ANNs are excellent at recognizing complex, nonlinear relationships in data and have been successfully used in a wide range of tasks, including regression, classification, and prediction.When used in drug discovery, ANNs can be trained on molecular descriptors, such as topological indices derived from chemical graph theory, to predict drug properties, such as solubility, toxicity, or biological activity.Topological indices capture structural information about molecules, including connectivity, branching, and molecular size, which is very relevant to the understanding of drug behavior.Using ANNs, researchers can develop predictive models that relate molecular structures to their properties, thereby accelerating the process of drug design.
However, one limitation of ANNs is that they are not interpretable, which is often referred to as the “black-box†problem.This makes it difficult to understand how single input features, such as topological indices, contribute to model predictions.Techniques, such as Shap Additive explanations (SHAP) can be applied to address this problem.SHAP is a technique used to explain the machine learning model output by assigning a value to each feature for its contribution to the predicted output.For ANNs trained on topological indices, SHAP can reveal the molecular features that most strongly contribute to the prediction of drug properties, offering valuable information for researchers and chemists.By combining the predictive power of ANNs and the interpretability of SHAP, this approach not only improves the accuracy of drug property predictions, but also the transparency and trustworthiness of the models, making them more valuable for scientific discovery and decision-making.
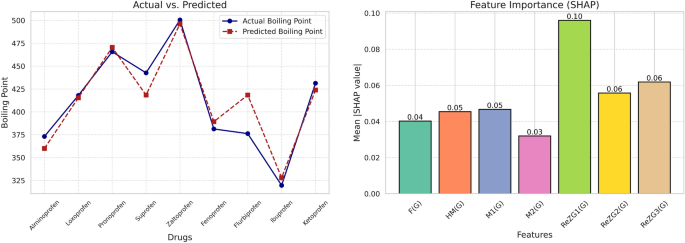
数字6shows a comparison between the actual and predicted values of a parameter, probably the boiling point, as indicated in Fig.6。The actual values are plotted against the predicted values on the left side of the plot, which are typically derived from an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) model.A comparison is necessary to ascertain the performance of the ANN model in predicting the boiling point or boiling point-related properties.The closer the predicted values are to the actual values, the better the model.The contributions of various topological indices to the prediction are displayed on the right-hand side of the graph.Topological indices are numerical quantities derived from the molecular structures from which physicochemical properties can be estimated.The graph likely shows which topological index contributes the most to the prediction accuracy.This is helpful in understanding the underlying parameters that the ANN model finds important to make a good prediction.
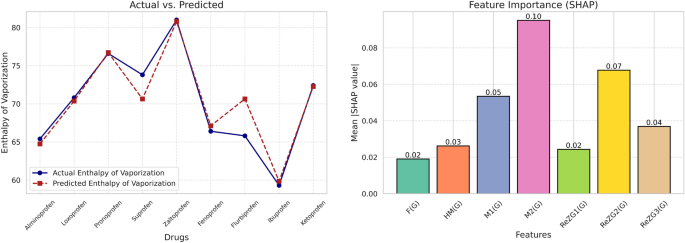
The left side of Fig.7compares the actual and predicted values of the enthalpy of vaporization for the various drugs.The close clustering of the points on the graph indicates good agreement between the predicted and actual values, attesting to the reliability of the model in predicting the enthalpy of vaporization.
The bar plot on the right displays the feature importance (based on the SHAP values) of the model.Among the topological indices considered, index\(M_2(G)\)contributes the most to the prediction, as the mean SHAP value is 0.10.This demonstrates the significance of\(M_2(G)\)in influencing the model’s predictions.Other indices, such asReZG2((g) 和\(M_1(G)\)have high contributions, whereas indices such asf((g) 和ReZG1(g) have relatively low contributions.
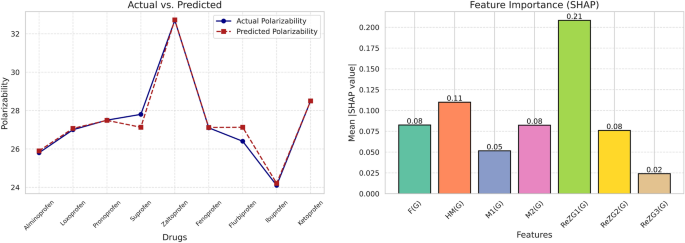
The left-hand side of Figure8shows a comparison between the actual and predicted polarizability values for various drugs.The plot illustrates a close agreement between the actual and predicted values, reflecting the success of the model in predicting polarizability.The bar plot on the right displays the feature importance (using the SHAP values) for the model.Among the topological indices considered, indexReZG3(g) contributes the most to the prediction, with an average SHAP value of 0.21.This reflects the dominant contribution ofReZG3(g) to the predictions of the model.Other indices, such as嗯((g) 和f((g) contribute significantly as well, whereas indices such asReZG2((g) 和\(M_1(G)\)have relatively smaller influences.
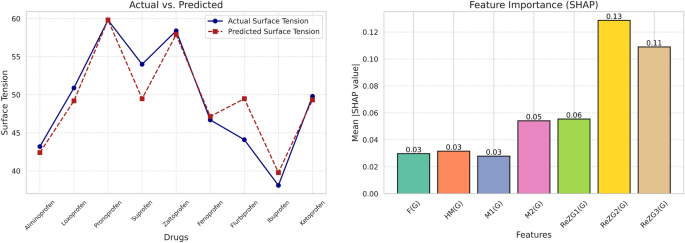
The left side of Figure9shows a comparison between the actual and predicted values of surface tension for various drugs.The match between the actual and predicted values confirmed the validity of the model for surface tension prediction.On the right-hand side, the bar plot shows the feature importance (based on the SHAP values) of the model.Among the topological indices, indexReZG2((g) contributes the most to the prediction, with a mean SHAP value of 0.13.This indicates the high contribution ofReZG2((g) to model performance.此外,ReZG3(g) 和\(M_2(G)\)also show notable contributions, whereasf((g) 和嗯((g) have lower contributions.
presents the predicted boiling point, enthalpy of vaporization, polarizability, and surface tension of the eight drugs using an Artificial Neural Network (ANN).The predictions span a variety of physical and chemical properties, illustrating the ability of the model to generate accurate predictions for several parameters.Alminoprofen:The model predicts a boiling point of\(360^{\circ }\)C, the lowest among all drugs.The enthalpy of vaporization is estimated to be 64.7 kJ/mol, polarizability 25.9, and surface tension 42.4 mN/m.All of these values indicate the intermediate physical and chemical properties of alminoprofen.
Loxoprofen:The boiling point of Loxoprofen is estimated at\(415.4^{\circ }\)C, and the enthalpy of vaporization is 70.4 kJ/mol.The polarizability was estimated to be 27.1, and the surface tension was 49.2 mN/m, indicating balanced properties among the tested drugs.
Pranoprofen:Pronoprofen possesses a boiling point of\(470.5^{\circ }\)C, which is among the higher boiling compounds.It also contains an enthalpy of vaporization of 76.7 kJ/mol, polarizability of 27.5, and surface tension of 59.8 mN/m, which are signs of strong physical properties.
Suprofen:The boiling point, vaporization enthalpy, and polarizability of Suprofen are predicted by the ANN as\(418.4^{\circ }\)C, 70.6 kJ/mol, and 27.1, respectively.It is predicted to have a surface tension of 49.5 mN/m, indicating properties similar to loxoprofen.
Zaltoprofen:Zaltoprofen possesses the highest calculated boiling point of\(496.3^{\circ }\)C and the highest polarizability of 32.7.It has an enthalpy of vaporization of 80.8 kJ/mol and a surface tension of 57.9 mN/m, reflecting its excellent physical properties.
Fenoprofen:Fenoprofen has a boiling point value of\(389.3^{\circ }\)C and an enthalpy of vaporization value of 67.1 kJ/mol.The polarizability was 27.1, and the surface tension was 47.2 mN/m, which is moderate when compared to other drugs.
Flurbiprofen:Calculated Flurbiprofen values include a boiling point of\(418.4^{\circ }\)C, enthalpy of vaporization at 70.6 kJ/mol, polarizability at 27.1, and surface tension at 49.5 mN/m.These values are close to those of suprofen, suggesting comparable properties.
布洛芬:Ibuprofen also possesses the lowest predicted surface tension of 39.8 mN/m and the lowest polarizability of 24.2.It boils at\(328^{\circ }\)C and has an enthalpy of vaporization of 59.8 kJ/mol, indicating that it has the weakest physical properties among the drugs.
Ketoprofen:The boiling point of ketoprofen is approximated as\(423.9^{\circ }\)C with the enthalpy of vaporization as 72.3 kJ/mol.It possesses 28.5 polarizability and 49.3 mN/m surface tension, with well-balanced characteristics for all the parameters.
presents a summary of the performance metrics of the ANN model, that is, the Mean Squared Error (MSE), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE), and R-square values for each property.The R-square values indicate the high accuracy of the predictions, i.e., 0.9 for the vaporization enthalpy and polarizability and 0.8 for, boiling point, and surface tension.Low RMSE values, i.e., 1.9 for polarizability and 2.5 for surface tension, also indicate the strength of the model.
Features were normalized before model training through min-max scaling to a range of [0, 1] to make them uniform and enhance model convergence.There was no feature selection algorithm used explicitly;however, topological indices that were selected were chosen on the basis of relevance as discussed in earlier studies.The artificial neural network has been implemented in Python with the TensorFlow platform (version 2.11).It was trained on a system that has an Intel Core i7 processor, 32 GB RAM, and NVIDIA RTX 3060 GPU.Chemical structure processing and descriptor calculations were done with RDKit (version 2023.03).
结论
In this study, we constructed a predictive model with artificial neural networks (ANNs) from molecular topological indices of a group of anti-inflammatory drugs.The model was able to predict physicochemical properties accurately, illustrating the usefulness of topological descriptors in computational drug modeling.The method, backed by carefully curated data sets and standard processing, supports the utility of ANNs in cheminformatics.As a potential avenue of further development, one could speculate on the extension of the method to larger drug classes or incorporation into personalized medicine or into high-throughput virtual screens.
数据可用性
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
参考
Pehlic, E. et al.Propionic acid derivatives synthesis as cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors by rheumatoid arthritis.
Feng, X., Ma, Z., Yu, C. & Xin, R. MRNDR: Multihead Attention-Based Recommendation Network for Drug Repurposing.化学信息与建模杂志 64(7), 2654–2669 (2024).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 Google Scholar一个
Jasim, H. H. & Abed, N. K. Determination of ibuprofen in Aqueaus solutions and pharmacokinetic preparations using UV-VIS spectrophotometry.Al-Nahrain Journal of Science 18(2), 1–9 (2015).
Li, X. et al.Screening for primary aldosteronism on and off interfering medications.内分泌 83(1), 178–187 (2024).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 Google Scholar一个
Rahimi-Tesiye, M., Rajabi-Maham, H., Hosseini, A. & Azizi, V. Beneficial effects of fenoprofen on cognitive impairment induced by the kindling model of epilepsy: Interaction between oxidative stress and inflammation.Brain Research Bulletin 220, 111151 (2025).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 Google Scholar一个
Zeng, Y. et al.GCCNet: A Novel Network Leveraging Gated Cross-Correlation for Multi-View Classification.IEEE多媒体交易 27, 1086–1099 (2025).
Saadeh, H. et al.Insights into the electronic structure of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Soft X-ray study of fenoprofen, ketoprofen, and methyl salicylate in the gas phase.Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 26(46), 29082–29094 (2024).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 Google Scholar一个
Zhang, R. et al.MvMRL: a multi-view molecular representation learning method for molecular property prediction.Briefings in Bioinformatics。25(4), bbae298 (2024).
Zhu, Y. et al.Flurbiprofen axetil is involved in basal-like breast cancer metastasis via suppression of the MEK/ERK signalling pathway.Cell Biology International 49(1), 68–78 (2025).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 Google Scholar一个
Huang, C., Liu, X., Wang, W., & Guo, Z. Exploring the Mechanism of Centipeda minima in Treating Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Based on Network Pharmacology.Current Computer - Aided Drug Design.(2024)。
Zubair, H. M. et al.Exploration of molecular interactions responsible for anti-inflammatory attributes of GI-friendly micro-sized formulation of flurbiprofen and clove oil.Inflammopharmacology。1–16.(2025)。
Hu, E. et al.A novel microbial and hepatic biotransformation-integrated network pharmacology strategy explores the therapeutic mechanisms of bioactive herbal products in neurological diseases: the effects of Astragaloside IV on intracerebral hemorrhage as an example.中药 18(1), 40 (2023).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 PubMed Central一个 Google Scholar一个
Alqudah, M., Stubbs, M. A., Al-Masaeed, M. & Fernandez, R. An evaluation of parents’ and caregivers’ preferences for managing fever in children based on experiences in using ibuprofen and paracetamol: a systematic review.Journal of Pediatric Nursing.(2025)。
Cheng, M. et al.A novel strategy of integrating network pharmacology and transcriptome reveals antiapoptotic mechanisms of Buyang Huanwu Decoction in treating intracerebral hemorrhage.民族药理学杂志 319, 117123 (2024).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 Google Scholar一个
Zhou, H. et al.Development of ibuprofen-modified fibroblast activation protein radioligands to improve cancer therapy.European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 283, 117115 (2025).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 Google Scholar一个
Lou, Y. et al.Effects of the CYP3A inhibitors, voriconazole, itraconazole, and fluconazole on the pharmacokinetics of osimertinib in rats.PeerJ 11, e15844 (2023).
Borah, A. R., Gogoi, M., Goswami, R., Nath, P. K. & Hazarika, S. Chiral Ni-Al LDH nanoparticle embedded electrospun nanofibrous membrane with high and stable permeance for enantioseparation of ketoprofen.Separation and purification technologies131443 (2025).
Peng, J., Ge, C., Shang, K., Liu, S. & Jiang, Y. Comprehensive profiling of the chemical constituents in Dayuanyin decoction using UPLC-QTOF-MS combined with molecular networking.Pharmaceutical Biology 62(1), 480–498 (2024).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 PubMed Central一个 Google Scholar一个
Moritake, K. et al.Equilibrium of monomers, dimers, and polymeric aggregates in the -aryl-propionic acid-type analgesics naproxen, ketoprofen, and ibuprofen: A comparative study with oxicam-type meloxicam and piroxicam.International Journal of Pharmaceutics。125167 (2025).
Lin, S. et al.A single-dose, randomized, open-label, four-period, crossover equivalence trial comparing the clinical similarity of the proposed biosimilar rupatadine fumarate to reference Wystamm in healthy Chinese subjects.Frontiers in Pharmacology 15, 1328142 (2024).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 PubMed Central一个 Google Scholar一个
Liu, M. et al.Preparation of colchicine combined with loxoprofen sodium loaded in dissolvable microneedles and its anti-gouty arthritis effect.Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 104, 106471 (2025).
CAS一个 Google Scholar一个
Hu, Q. et al.VARFVV: View-Adaptive Real-Time Interactive Free-View Video Streaming with Edge Computing.IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications.(2025)。
Ono, R. & Horibata, K. Four cases of calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease presenting with polymyalgia-like symptoms and chondrocalcinosis in the shoulder and hip joints were identified using CT imaging.肉质。17(1) (2025).
Chen, X. & Jing, R. Video super resolution based on deformable 3D convolutional group fusion.科学报告 15(1), 9050 (2025).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 PubMed Central一个 Google Scholar一个
Jin, Y. et al.An innovative guanidinium-based ionic covalent organic framework with abundant aromatic rings for high-efficiency naproxen removal: Adsorption behavior, mechanisms, and density functional theory calculations.Separation and Purification Technology 357, 130182 (2025).
CAS一个 Google Scholar一个
Zhao, X. et al.Comparison of the efficacy and safety of low-dose antihypertensive combinations in patients with hypertension: protocol for a systematic review and network meta-analysis.BMJ Open 14(10), e086323 (2024).
Aliyu, A. A. et al.Novel Cd (II) complexes bearing naproxen and imidazole ligands: synthesis, single-crystal X-ray, structural elucidation, quantum chemical investigation, molecular docking, antioxidant, and antimicrobial screening.多面体 265, 117281 (2025).
CAS一个 Google Scholar一个
Li, B. et al.Broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory and antioxidant therapy of inflammatory-storm actuated diseases via programmable self-derived cryo-dead neutrophils.化学工程杂志 507, 160643 (2025).
CAS一个 Google Scholar一个
Zhang, E., Sun, M. & Gao, L. Rh (III)-Catalyzed Double Annulation of 3-Phenyl-1, 2, 4-Oxadiazoles with 2-Diazo-1, 3-diketones: Access to Pyran-Fused Isoquinolines.分子 30(1), 149 (2025).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 PubMed Central一个 Google Scholar一个
Xie, X., Chen, J., Que, R. & Xu, C. Efficacy of tobramycin dexamethasone combined with pranoprofen in middle-aged and elderly patients with post-cataract and the value of improving inflammatory factor levels.American Journal of Translational Research 16(9), 5011 (2024).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 PubMed Central一个 Google Scholar一个
Thakur, S. et al.Medicinal chemistry-based perspective on thiophene and its derivatives: Exploring structural insights to discover plausible druggable leads.RSC Medicinal Chemistry.(2024)。
Noyman, D. B. E., Sommer, A. C., Naaman, E., Gonzalez-Lugo, J. H. & Mimouni, M. Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the management of pain after PRK: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Journal of Cataract & Refractive Surgery 50(10), 1083–1091 (2024).
Green, G. A. Understanding NSAIDs: From Aspirin to COX-2.临床基石 3(5), 5059 (2001).
Rao, C. V. & Reddy, B. S. NSAIDs and chemoprevention.Curr。Cancer Drug Targets 4(1), 2942 (2004).
Cashman, J. N. Mechanisms of Action of NSAIDs in Analgesia.毒品 52(5), 1323 (1996).
De Felice, F. G. & Ferreira, S. T. Beta-amyloid production, aggregation, and clearance as targets for therapy in Alzheimer s disease.细胞。摩尔。Neurobiol. 22(6), 545563 (2002).
Harkany, T. et al.Mechanisms of Beta-Amyloid Neurotoxicity: Perspectives of Pharmacotherapy.Rev. Neurosci。11(4), 329-382 (2000).El-Agnaf, O. M., Mahil, D. S., Patel, B. P. & Austen, B. Oligomerization and Toxicity of Beta-Amyloid-42 are Implicated in Alzheimer s disease.
生物化学。生物。res。社区。 273(3), 1003–1007 (2000).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 Google Scholar一个
Podlisny, M. B. et al.Oligomerization of endogenous and synthetic amyloid beta-protein at nanomolar levels in cell culture and stabilization of monomers by Congo red.生物化学 37(11), 3602–3611 (1998).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 Google Scholar一个
Agdeppa, E. D. et al.In Vitro Detection of (S)-naproxen and ibuprofen binding to plaques in the Alzheimer s brain using the positron emission tomography molecular imaging probe 2-(1-6-[(2-[18F] fluoroethyl)(methyl)Amino]-2-Naphthylethylidene) malononitrile.神经科学 117(3), 723–730 (2003).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 Google Scholar一个
Talaga, P. Beta-amyloid aggregation inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer s disease: dreams or reality?.Mini Rev. Med.化学 1(2), 175–186 (2001).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 Google Scholar一个
Thomas, T., Nadackal, T. G. & Thomas, K. Aspirin and Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Inhibit Amyloid-Beta Aggregation.Neuroreport 12(15), 3263–3267 (2001).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 Google Scholar一个
Gutman, I. & Polansky, O. E. Mathematical concepts in organic chemistry.Springer Science and Business Media.(2012年)。
Furtula, B. & Gutman, I. A forgotten topological index.Journal of mathematical chemistry 53(4), 1184–1190 (2015).
MathScinet一个 CAS一个 Google Scholar一个
Rajasekharaiah, G. V. & Murthy, U. P. Hyper-Zagreb indices of graphs and their applications.Journal of Algebra Combinatorics Discrete Structures and Applications 8(1), 9–22 (2021).
Ranjini, P. S., Lokesha, V. & Usha, A. Relation between phenylene and hexagonal squeez using harmonic index.int。J. Graph Theory 1(3), 116–121 (2013).
Shirakol, S., Kalyanshetti, M. & Hosamani, S. M. QSPR analysis of certain distance based topological indices.应用数学和非线性科学 4(2), 371–386 (2019).
Gnanaraj, L. R. M., Ganesan, D. & Siddiqui, M. K. Topological indices and QSPR analysis of NSAID drugs.Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds 43(10), 9479–9495 (2023).
CAS一个 Google Scholar一个
Khan, A., Zhong, Y., Arif, A., Zada, L. & Fang, M. Computational and topological properties of neural networks by means of graph-theoretic parameters.Alexandria Engineering Journal 66, 957–977 (2023).
Mahadi, H., Alanazi, S. J. & Wang, S. Predictive potential of eigenvalues-based graphical indices for determining thermodynamic properties of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with applications to polyacenes.Computational Materials Science 238, 112944 (2024).
Hayat, S. & Imran, M. On topological properties of nanocones CNCk [n].Studia Universitatis Babes-Bolyai Chemia 59(4), 113–128 (2014).
广告一个 Google Scholar一个
Almohanna, N. E. et al.Investigating topological descriptor and Gibb s energy for semiconducting carbon allotrope through advanced curve fitting model.科学报告 15(1), 12561 (2025).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 PubMed Central一个 Google Scholar一个
Huang, L., Alhulwah, K. H., Hanif, M. F., Siddiqui, M. K. & Ikram, A. S. On QSPR analysis of glaucoma drugs using machine learning with XGBoost and regression models.Computers in Biology and Medicine 187, 109731 (2025).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 Google Scholar一个
Tamilarasi, W. & Balamurugan, B. J. QSPR and QSTR analysis to explore pharmacokinetic and toxicity properties of antifungal drugs through topological descriptors.科学报告 15(1), 1–25 (2025).
Qin, H. et al.On QSPR analysis of pulmonary cancer drugs using python-driven topological modeling.科学报告 15(1), 3965 (2025).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 PubMed Central一个 Google Scholar一个
Hakeem, A., Ullah, A., Zaman, S., Hamed, Y. S. & Belay, M. B. Computational insights into flavonoid molecular structures and their QSPR modeling via degree based molecular descriptors.Chemical Papers 79(2), 745–760 (2025).
CAS一个 Google Scholar一个
Qin, H. et al.A python approach for prediction of physicochemical properties of anti-arrhythmia drugs using topological descriptors.科学报告 15(1), 1742 (2025).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 PubMed Central一个 Google Scholar一个
Arockiaraj, M., Jeni Godlin, J. J., Radha, S., Aziz, T. & Al-Harbi, M. Comparative study of degree, neighborhood and reverse degree based indices for drugs used in lung cancer treatment through QSPR analysis.科学报告 15(1), 3639 (2025).
CAS一个 PubMed一个 PubMed Central一个 Google Scholar一个
致谢
This work was supported and funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University (IMSIU) (grant number IMSIU-DDRSP2502).
道德声明
竞争利益
作者没有宣称没有竞争利益。
附加信息
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
权利和权限
开放访问This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material.您没有根据本许可证的许可来共享本文或部分内容的改编材料。The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material.If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.To view a copy of this licence, visithttp://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/。重印和权限
引用本文
Ahmed, W.E., Hanif, M.F., Siddiqui, M.K.
等。Advanced QSPR modeling of profens using machine learning and molecular descriptors for NSAID analysis.Sci代表15 , 26356 (2025).https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-09878-z
已收到:
公认:
出版:
doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-09878-z